Ticks on Dogs

Ticks are parasitic arachnids that latch onto dogs to feed on their blood. They are not just a nuisance; they pose significant health risks by transmitting diseases. Understanding ticks, their impact, and methods to prevent them is essential for your dog’s well-being.
Identifying Ticks
Ticks vary in size, from as small as a sesame seed to as large as a pea when engorged with blood. They can be brown, black, or reddish, depending on the species and life stage. Ticks attach firmly to the dog’s skin, typically found around the head, ears, neck, paws, and belly.
Diseases Transmitted by Ticks
Ticks carry several diseases that can severely affect your dog’s health:
1. Lyme Disease
-
Caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted mainly by the deer tick (black-legged tick).
-
Symptoms include fever, lethargy, swollen joints, limping, loss of appetite, and in severe cases, kidney failure.
2. Ehrlichiosis
-
Spread primarily by the brown dog tick.
-
Common symptoms include fever, weight loss, lethargy, swollen lymph nodes, bleeding disorders, and neurological signs.
3. Anaplasmosis
-
Transmitted by deer ticks and western black-legged ticks.
-
Symptoms include fever, joint pain, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite.
4. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
-
Spread by American dog ticks, wood ticks, and brown dog ticks.
-
Symptoms include high fever, muscle pain, vomiting, diarrhea, swelling of the face or legs, and in severe cases, neurological issues or organ damage.
5. Babesiosis
-
Caused by microscopic parasites infecting red blood cells.
-
Symptoms include anemia, pale gums, lethargy, jaundice, dark urine, and rapid breathing.
Symptoms of a tick infestation
Ticks can cause significant discomfort and potentially severe health issues for dogs. Recognizing the symptoms of a tick infestation early is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment. Here are common signs that your dog might have ticks:
1. Visible Ticks on the Skin
-
The most obvious sign is spotting ticks attached to your dog’s skin, usually around the head, ears, neck, paws, or belly.
-
Ticks vary in size from tiny and difficult to spot, to larger, engorged ticks after feeding.
2. Frequent Scratching or Licking
-
Dogs infested with ticks often scratch, lick, or chew at certain areas, indicating irritation or discomfort caused by tick bites.
3. Redness or Swelling
-
Tick bites can cause redness, swelling, or inflammation at the attachment site.
-
You might notice small bumps or scabs where ticks have previously attached.
4. Skin Irritation and Hair Loss
-
Persistent scratching and biting due to tick irritation can lead to hair loss, inflamed skin, and potentially secondary infections.
5. Lethargy or Weakness
-
A dog with multiple tick bites or a severe infestation may exhibit signs of fatigue, weakness, or general lethargy.
6. Loss of Appetite
-
Dogs may experience reduced appetite due to discomfort, inflammation, or underlying tick-borne diseases.
7. Fever or Illness Symptoms
-
Ticks carry diseases that can lead to fever, joint pain, swelling, difficulty walking, or signs of neurological issues.
-
Dogs might also show other illness symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, or breathing difficulties.
8. Pale Gums
-
In severe cases, especially if the infestation has led to significant blood loss or anemia, dogs may have pale gums or rapid breathing.
Topical Tick Treatments
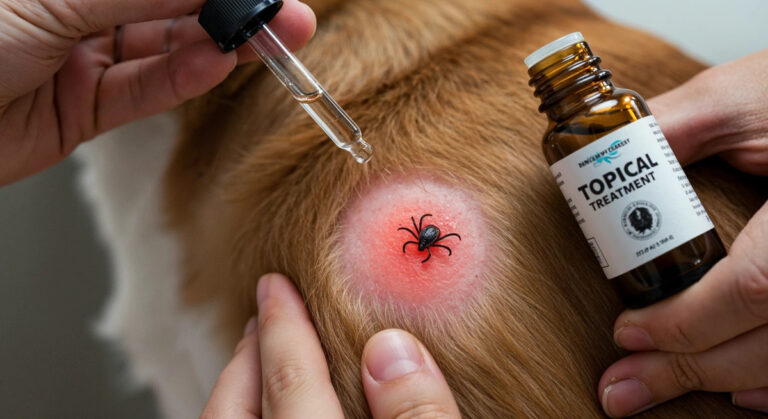
Topical tick treatments, commonly referred to as “spot-on” treatments, are medications applied directly onto a dog’s skin to protect against ticks and other parasites. These treatments are widely used due to their convenience, effectiveness, and ease of application.
How Topical Treatments Work:
-
Topical treatments contain active ingredients that spread over the dog’s body through the skin’s natural oils, providing protection by killing and repelling ticks upon contact.
-
Typically applied monthly, these treatments offer ongoing protection against ticks.
Advantages of Topical Tick Treatments:
-
Convenience: Simple and quick application at home.
-
Long-lasting Protection: Usually provides protection for up to one month per application.
-
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Often effective against multiple parasites, including fleas, lice, mites, and mosquitoes.
-
Water-Resistant: Many topical treatments remain effective even if the dog gets wet or swims occasionally.
Disadvantages of Topical Tick Treatments:
-
Potential Skin Irritation: Some dogs may experience redness, irritation, or allergic reactions at the application site.
-
Toxicity Risks: Incorrect application or dosage, especially on small dogs or puppies, can lead to adverse reactions.
-
Reduced Effectiveness with Frequent Bathing: Frequent bathing or swimming can diminish effectiveness, requiring reapplication sooner.
-
Environmental Transfer: Medication residue can transfer onto humans or household surfaces, posing minor exposure risks.
Application Tips:
-
Apply the treatment directly onto the skin between your dog’s shoulder blades or along the spine to prevent licking.
-
Avoid bathing your dog 48 hours before and after application to maximize effectiveness.
-
Ensure correct dosing based on your dog’s weight and health status.
Safety Considerations:
-
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely.
-
Monitor your dog after application for any signs of irritation or adverse reactions.
-
Consult your veterinarian, especially if your dog has sensitive skin, underlying health issues, or is a puppy or senior dog.
Oral Tick Treatments
Oral tick treatments are medications administered by mouth to protect dogs from ticks and related parasites. These treatments are often available as flavored chewable tablets or pills, making them easy for most dogs to accept.
How Oral Tick Treatments Work:
-
Oral tick treatments enter the bloodstream after ingestion, providing systemic protection.
-
Ticks that bite your dog ingest the medication and quickly die, significantly reducing the risk of disease transmission.
Advantages of Oral Tick Treatments:
-
Convenient Administration: Easy and straightforward to give at home, typically available as tasty chews that dogs willingly accept.
-
Fast-Acting: Starts killing ticks within hours of administration, quickly reducing the risk of tick-borne diseases.
-
Effective and Consistent Dosage: Ensures accurate dosing, providing reliable protection without concerns about application errors or environmental residue.
-
Unaffected by Bathing or Swimming: Effectiveness remains consistent regardless of your dog’s bathing or swimming habits.
Disadvantages of Oral Tick Treatments:
-
Potential Side Effects: Some dogs may experience mild gastrointestinal upset, including vomiting, diarrhea, or loss of appetite after taking oral medications.
-
Limited Spectrum: Certain oral treatments may exclusively target ticks and fleas, requiring additional medications to cover other parasites.
-
Regular Administration Required: Oral treatments typically need monthly or quarterly dosing to maintain continuous protection.
-
Risk of Rare Reactions: Though uncommon, some dogs may exhibit serious adverse reactions, such as lethargy, neurological symptoms, or seizures.
Administration Tips:
-
Provide oral treatments alongside meals or treats to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
Follow the recommended dosing schedule strictly, as missing doses can significantly decrease effectiveness.
-
Monitor your dog closely after administering the medication, especially during initial treatments, to observe any adverse reactions.
Safety Considerations:
-
Consult your veterinarian before starting oral tick treatments, especially for puppies, elderly dogs, or those with existing health conditions.
-
Always use veterinarian-approved products and adhere to recommended dosages based on your dog’s weight and health.
-
Promptly report any adverse reactions to your veterinarian.
Tick Collars

Tick collars are wearable devices designed to provide dogs with ongoing protection against ticks. These collars release active ingredients that repel and kill ticks, helping to reduce the risk of infestation and tick-borne diseases.
How Tick Collars Work:
-
Tick collars continuously release active substances onto your dog’s skin and coat, spreading through natural oils.
-
The ingredients either repel ticks from attaching or kill them upon contact, providing extended protection.
Advantages of Tick Collars:
-
Long-lasting Protection: Many collars offer continuous protection ranging from several months up to eight months.
-
Ease of Use: Simply place the collar around your dog’s neck; minimal effort is required for ongoing protection.
-
Cost-effective: Often more economical in the long term compared to monthly topical or oral treatments.
-
Water-Resistant Options: Some collars remain effective even if your dog swims or gets wet occasionally.
Disadvantages of Tick Collars:
-
Potential Skin Irritation: Some dogs may experience redness, itching, or allergic reactions around the neck area.
-
Limited Coverage Area: Effectiveness might diminish toward the hindquarters, requiring additional treatments for comprehensive protection.
-
Safety Risks if Improperly Fitted: An improperly fitted collar can cause discomfort or potential injury.
-
Chemical Exposure Concerns: Continuous exposure to the active ingredients may be a concern for some dog owners, particularly if young children or other pets frequently interact closely with the dog.
Proper Use and Application Tips:
-
Ensure the collar fits snugly but comfortably around your dog’s neck, allowing space for two fingers to fit underneath.
-
Regularly inspect and adjust the collar as your dog grows or changes weight.
-
Replace the collar according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule to maintain protection.
Tips for Tick Prevention
Effective tick prevention involves a combination of methods, from regular grooming to environmental management. Here are essential tips to help prevent tick infestations and protect your dog:
Regular Use of Preventatives:
-
Consistently use veterinarian-approved tick preventatives, including collars, topical treatments, or oral medications.
-
Maintain a regular treatment schedule to ensure continuous protection.
Routine Checks:
-
Frequently inspect your dog’s fur, especially after outdoor activities.
-
Pay close attention to tick-prone areas like ears, neck, paws, underbelly, and tail.
Grooming and Bathing:
-
Regular grooming and brushing help detect and remove ticks early.
-
Use veterinarian-approved shampoos designed for tick prevention.
Environmental Management:
-
Regularly mow lawns, trim bushes, and clear away leaf piles and debris to reduce tick habitats.
-
Use pet-safe tick repellents or treatments around your yard, particularly in shaded and damp areas.
Limit Exposure:
-
Limit your dog’s exposure to wooded areas, high grasses, or places known to have high tick populations.
-
Keep your dog on trails during walks and hikes to minimize contact with ticks.
Immediate Removal:
-
Quickly and safely remove any ticks you find using tweezers or tick removal tools.
-
Proper tick removal reduces the risk of disease transmission.
Regular Veterinary Visits:
-
Schedule routine check-ups and discuss tick prevention strategies tailored specifically to your dog’s lifestyle and environment.
-
Consider vaccinations against tick-borne diseases if recommended by your veterinarian.
Implementing these comprehensive tick prevention strategies will significantly reduce the risk of infestations and help maintain your dog’s health and well-being.



